对于现代集约化养殖,烈性疫病正在得到良好控制,所以在一定程度上来讲,鸡群免疫力就是生产力。传染性法氏囊病(infectious bursal disease,IBD)是由传染性法氏囊病病毒(infectious bursal disease virus,IBDV)引起的一种危害雏鸡的最严重的急性免疫抑制病,感染鸡3-5天内急性发病,超强毒株的致死率高达60%以上,是养禽业健康发展的重要威胁之一。上世纪80年代末以来,该病的优势流行毒株一直是IBDV超强毒株(very virulent IBDV,vvIBDV),随着饲养管理水平和疫苗的使用,vvIBDV正在逐步得到控制。
然而近年来,不直接致死鸡但导致严重免疫抑制的非典型IBD在包括中国在内的东亚地区的免疫鸡群中突然出现,造成了严重的经济损失。中国农业科学院哈尔滨兽医研究所禽免疫抑制病团队祁小乐研究员小组率先揭示了非典型IBD的病原是基因型为A2dB1的IBDV新型变异株(novel variant IBDV,nVarIBDV)。近日,该研究小组进一步揭示了nVarIBDV因免疫逃逸而在免疫鸡群中广泛流行的原因和分子机制,相关研究结果以题为“Residues 318 and 323 in capsid protein are involved in immune circumvention of the atypical epizootic infection of infectious bursal disease virus”的长文发表于《Frontiers in Microbiology》上(原文链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35966653/)。

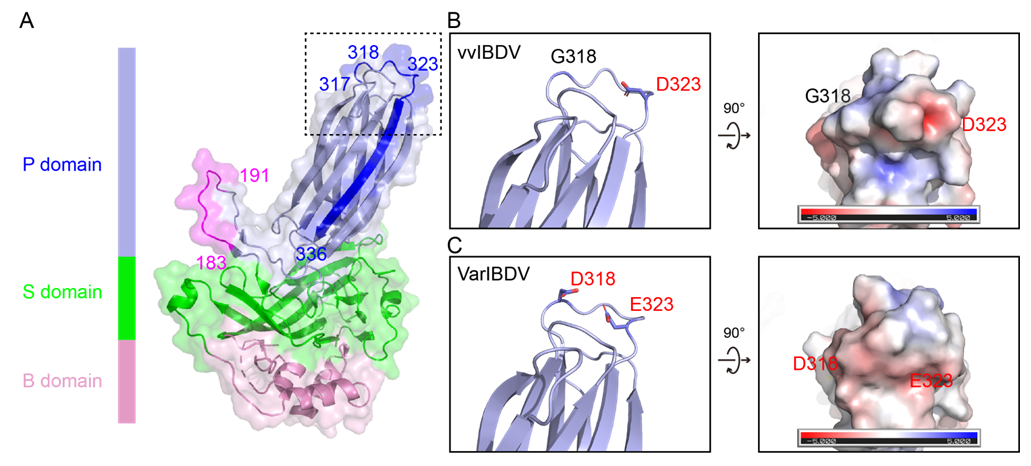
由于抗原不匹配,nVarIBDV在一定程度上可以逃逸现有的针对vvIBDV的疫苗的免疫保护。研究数据显示,vvIBDV抗血清对nVarIBDV的中和效价降低了7.0 log2,而nVarIBDV抗血清对vvIBDV的中和效价降低了3.2 log2,正反两反面的数据充分说明当前IBDV的两大流行株抗原性差异明显。同时发现,一株对vvIBDV具有良好中和活性的单克隆抗体(单抗)2-5C-6F不能够识别nVarIBDV。
该研究进一步鉴定了2-5C-6F株单抗的抗原表位位于病毒衣壳蛋白VP2上,发现nVarIBDV和vvIBDV在该表位上有两个氨基酸差异:G318D和D323Q。基于蛋白系列突变体的试验显示,318和323位氨基酸显著影响了单抗2-5C-6F对nVarIBDV和vvIBDV的识别和结合,基于反向遗传操作的系列突变病毒也证明了这一点。进而,由单抗2-5C-6F介导的交叉中和试验表明,318和323位氨基酸突变也影响单抗2-5C-6F对IBDV的中和。
进一步的数据还表明,318和323位氨基酸甚至还显著影响了抗血清对IBDV的中和。318和323位氨基酸位于IBDV衣壳蛋白的PHI Loop区的最外侧,其突变可能影响了局部电势和IBDV的衣壳结构。综上,衣壳蛋白VP2的318和323位氨基酸差异是nVarIBDV在免疫鸡群广泛流行的重要原因之一。
2019年以来,祁小乐研究员小组提出了IBDV新的基因分型方法,率先鉴定了非典型IBD的病原为A2dB1型nVarIBDV,系统研究了nVarIBDV致病性等生物学性状,解析了nVarIBDV溯源问题和流行原因,阐明了我国IBDV的流行新态势;合作解析了迄今分辨率最高的IBDV不同毒力毒株的原子水平粒子结构;创制了首个IBD反向遗传疫苗、首个IBD新型变异株亚单位疫苗等禽免疫抑制病防控新技术和新制剂。这些研究明确了非典型IBD的病原特征,揭示了其免疫逃逸和免疫抑制的分子机制,创制了抗原性匹配的防治新技术,对禽免疫抑制病的综合防控和养禽业的健康发展具有重要意义。
近三年发表的相关文章如下:
[1]Fan LJ, et al. Residues 318 and 323 in capsid protein are involved in immune circumvention of the epidemic atypical infection of infectious bursal disease virus. Frontiers Microbiology, 2022, 13: 909252.
[2]Zhang WY, et al. The over-40-years-epidemic of infectious bursal disease virus in China. Viruses, 2022, 14, 2253.
[3]Bao KY, et al. Cryo-EM structures of infectious bursal disease virus with different virulence provide insights on their assembly and invasion. Science Bulletin, 2022, 67:646-654.
[4]Jiang N, et al. Genotyping and molecular characterization of infectious bursal disease virus identi?ed in important poultry-raising areas of China during 2019 and 2020. Front. Vet. Sci., 2021, 8:759861.
[5]Wang YL, et al. An improved scheme for infectious bursal disease virus genotype classification based on both genome-segments A and B. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2021, 20(5): 1372-1381.
[6]Wang YL, et al. Identification and pathogenicity evaluation of a novel reassortant infectious bursal disease virus (Genotype A2dB3). Viruses, 2021, 13(9):1682.
[7]Jiang N, et al. Naturally occurring mutated infectious bursal disease virus of genotype A8B1 associated with bursa damage in China. Virus Research, 2021, 302:198498.
[8]Wang Y, et al. Development of a viral‐like particle candidate vaccine against novel variant infectious bursal disease virus. Vaccines, 2021, 9(2):142.
[9]Fan LJ, et al. Novel variant infectious bursal disease virus suppresses Newcastle disease vaccination in broiler and layer chickens. Poultry Science, 2020, 99:6542-6548.
[10]Fan LJ, et al. A reassortment vaccine candidate of the novel variant infectious bursal disease virus. Veterinary Microbiology, 2020, 251: 108905.
[11]Fan LJ, et al. Novel variants of infectious bursal disease virus can severely damage the bursa of fabricius of immunized chickens. Veterinary Microbiology, 2020, 240:108507.
[12]Wang YL, et al. Naturally occurring cell-adapted classic strain of infectious bursal disease virus. Veterinary Microbiology, 2020, 243: 108620.
[13]Wu TT, et al. Naturally occurring homologous recombination between novel variant infectious bursal disease virus and intermediate vaccine strain. Veterinary Microbiology, 2020, 245, 108700.
[14]Fan LJ, et al. Novel variant strains of infectious bursal disease virus isolated in China. Veterinary Microbiology, 2019, 230:212-220.

一周阅读排行